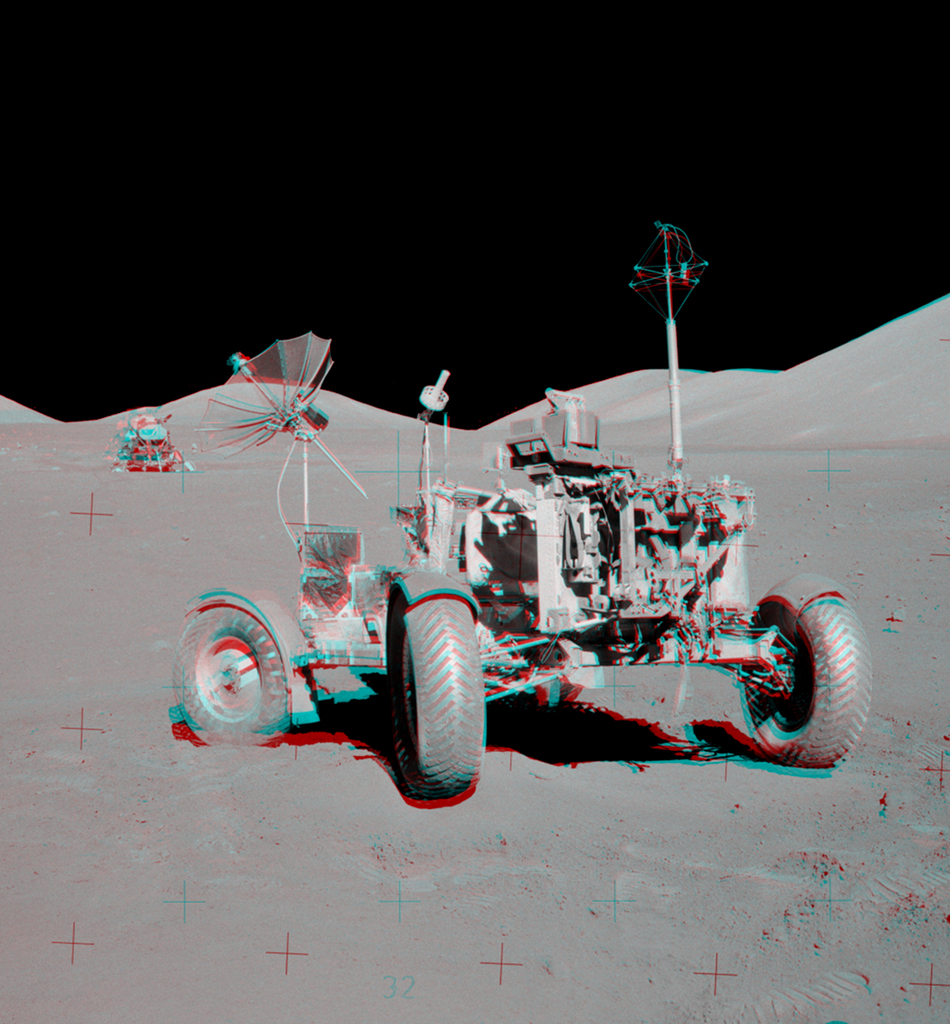
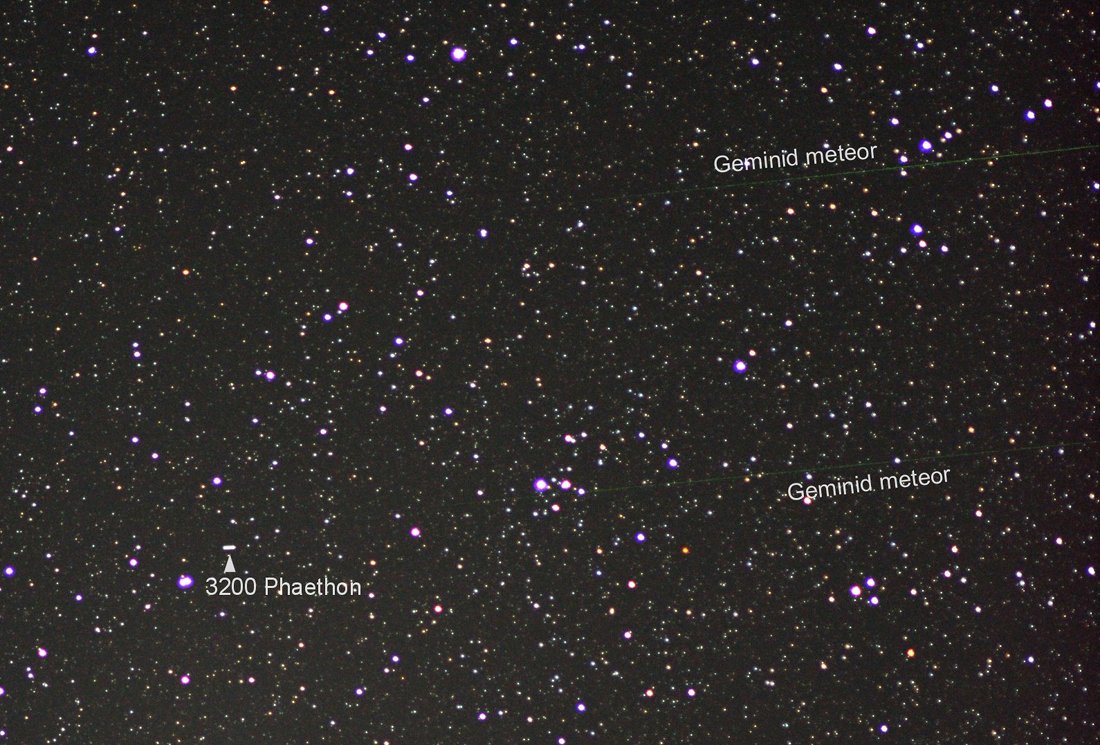
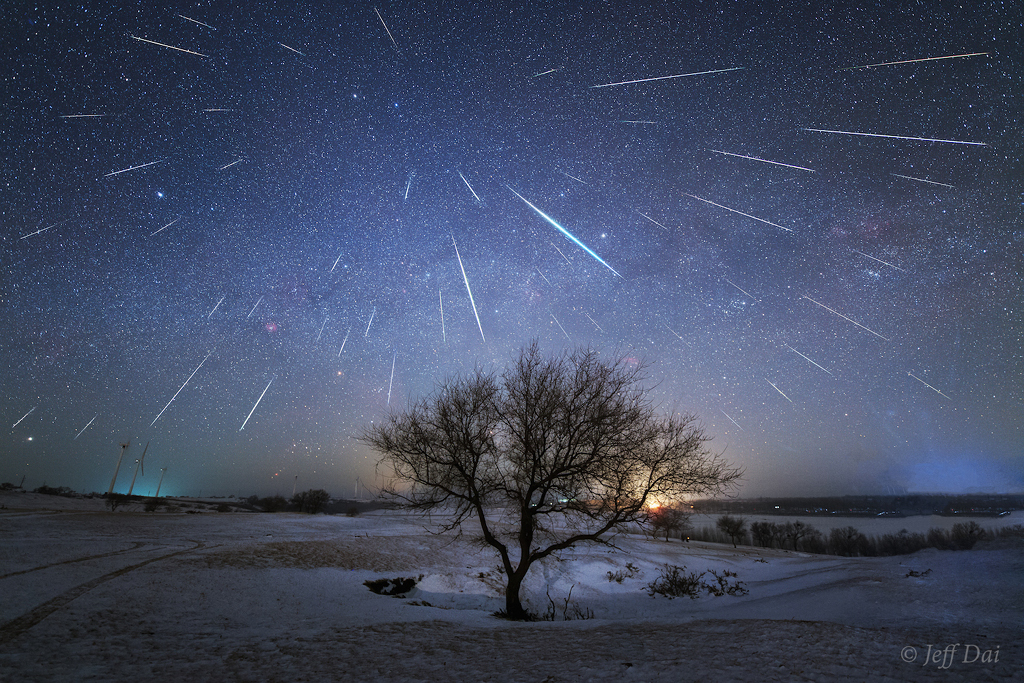
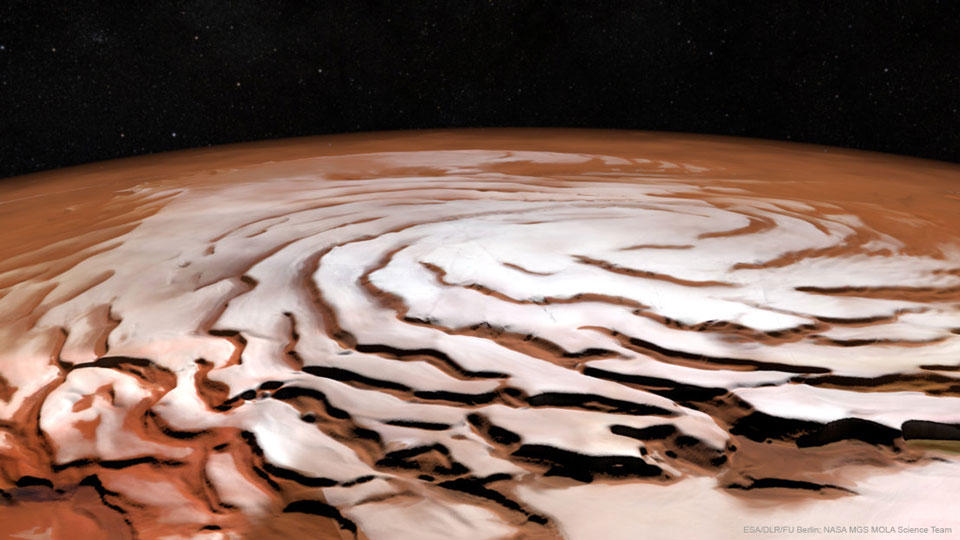
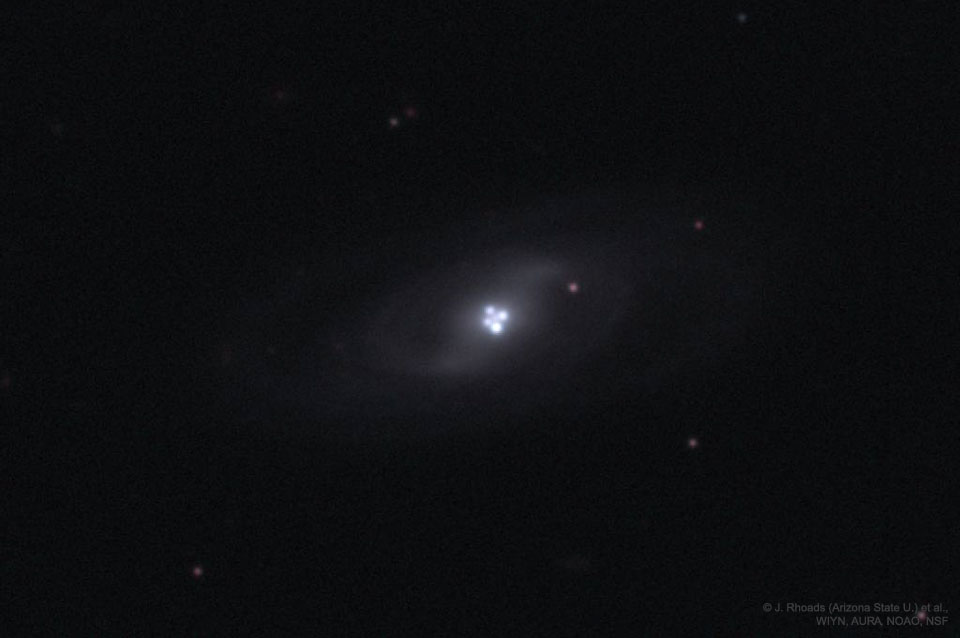
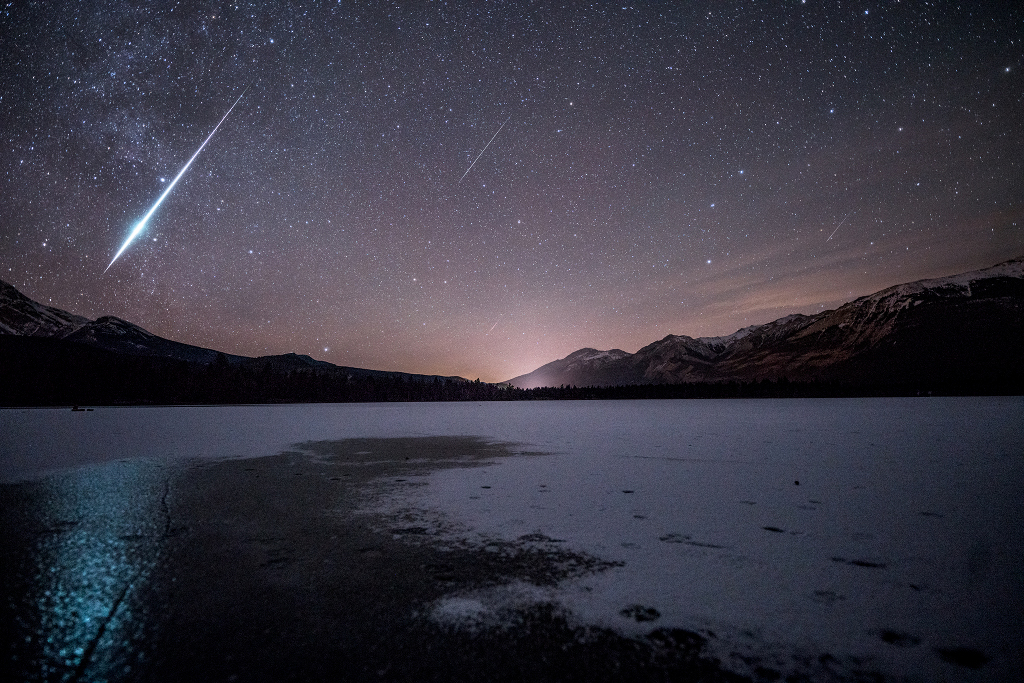
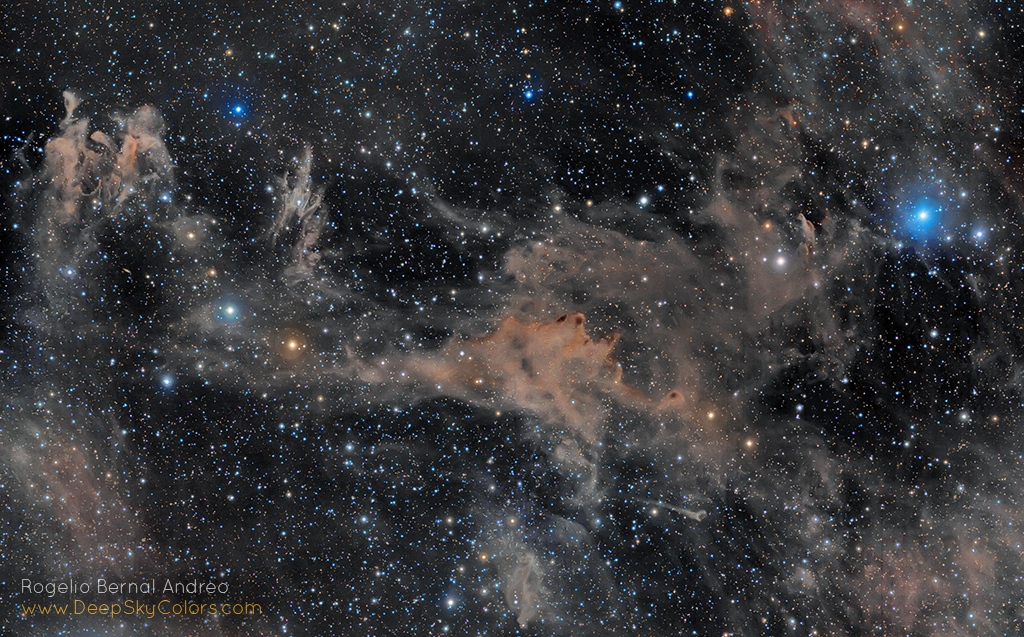
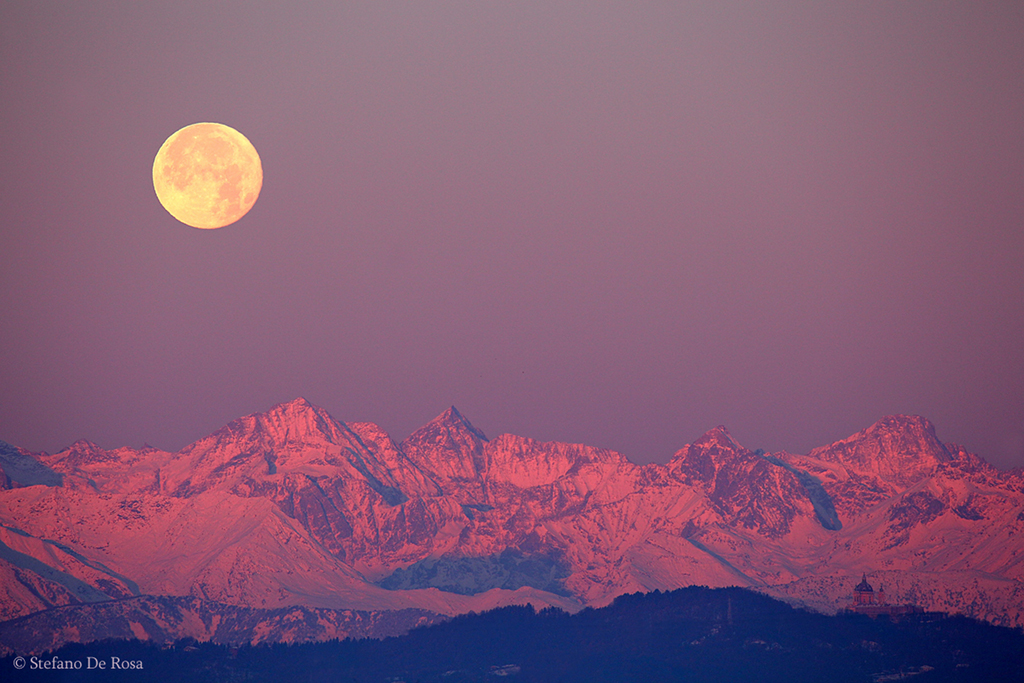
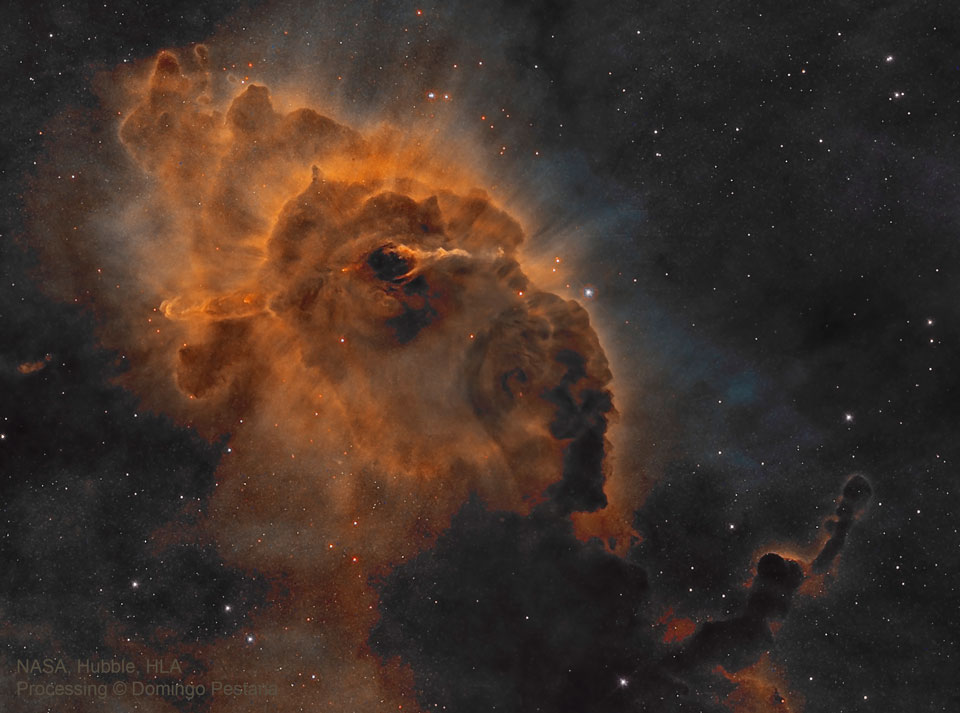
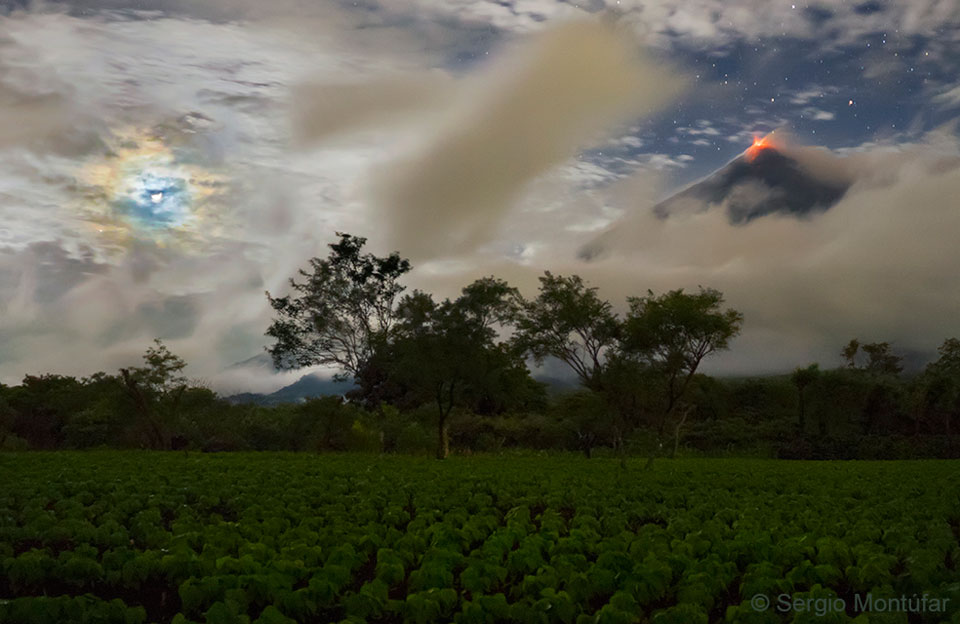
Get out your red/blue glasses and check out this stereo scene from Taurus-Littrow valley on the Moon! The color anaglyph features a detailed 3D view of Apollo 17's Lunar Rover in the foreground -- behind it lies the Lunar Module and distant lunar hills. Because the world was going to be able to watch the Lunar Module's ascent stage liftoff via the rover's TV camera, this parking place was also known as the VIP Site. In December of 1972, Apollo 17 astronauts Eugene Cernan and Harrison Schmitt spent about 75 hours on the Moon, while colleague Ronald Evans orbited overhead. The crew returned with 110 kilograms of rock and soil samples, more than from any of the other lunar landing sites. Cernan and Schmitt are still the last to walk (or drive) on the Moon. via NASA http://ift.tt/2pRX9zr